Fine lines, wrinkles, uneven skin tone, and acne? You may want to consider adding tretinoin to your routine.
Today, I’ll walk you through everything you need about tretinoin, which is the key to dreamy-looking skin!
Tretinoin is known for its exceptional ability to turn back the hands of time. With its prowess in stimulating collagen production and promoting skin cell turnover, tretinoin effortlessly diminishes fine lines and wrinkles, leaving behind a rejuvenated and resilient complexion.
Used correctly, tretinoin can make a big difference in skin health and well-being for many people. Here’s what you need to know about how it works, if it suits you, and how to use it.
[Editor’s note: Retinoids shouldn’t be used by those who are pregnant, considering getting pregnant, or nursing. Please consult with your doctor before use.]
The Tretinoin Guide:
What Is Tretinoin and How Does it Work?
First approved by the FDA as a treatment for acne 40 years ago, it quickly became apparent that tretinoin went beyond acne treatment to make the skin as a whole significantly smoother, brighter, and less wrinkled.
Tretinoin is a biologically active form of vitamin A that is extensively proven in treating acne and sun-induced skin aging.
It is a type of retinoic acid already found in the human body. When used as a pharmaceutical, retinoic acid binds to switches inside skin cells called retinoid receptors. This triggers the receptor to change how genes in the cell express themselves.
So retinoids “reset” the cell to start acting normally again if it’s been off doing something stupid like producing too much oil or making the skin wrinkle.
Retinoid Types
The most established anti-aging actives are retinoids, a group of compounds derived from vitamin A.
Simply put, a retinoid is a class of chemical compounds that either contain vitamin A or are chemically related to it. There are three primary categories of retinoids, but the ones most commonly found in skincare products include many first-generation retinoids, including retinol and tretinoin.
Vitamin A was initially used to treat acne. However, during its use, it was found to have second-to-none, scientifically proven abilities to reverse and prevent the signs of aging.
There is no other ingredient out there that can compete with vitamin A and its incredible abilities!
Retinoids are also some of the most studied ingredients for restoring photo-damaged skin. While research has shown that they can be good anti-aging ingredients, their limitations hinder their effectiveness. In the case of tretinoin, the anti-aging results may require a very long period to take effect, which can frustrate many people looking for an improvement in the appearance of their skin.
Additionally, there are many cases of adverse effects related to the use of tretinoin and retinol, including skin irritation and dermatitis. While retinol may produce fewer occurrences of skin irritation than tretinoin, this ingredient may be as much as 20 times less potent, thus leading to less efficacy.
Over the decades, retinoids have been the subject of well-designed medical studies showing all kinds of compound uses:
- They can reduce the number and depth of fine lines and wrinkles;
- They can prevent acne;
- They can fade hyperpigmentation and acne scars;
- They can unclog pores and reduce the appearance of pores;
- They can treat psoriasis and keratosis pilaris;
- They are even used to treat certain types of skin cancer and precancerous cells.
Retinoid Conversion Pathway
Retinoic acid is the active form that the skin can use. Therefore, all retinoids must convert into retinoic acid.
There are, of course, exceptions to this. Some ingredients don’t require conversion into retinoic acid to be active, but we will look at this further down.
For retinoids to affect fine lines, texture, and pigmentation, retinoic acid must bind to the retinoid receptors in our bodies. When this happens, cellular renewal and cellular repair processes are undertaken.
Within our skin, this conversion to retinoic acid is carried out by enzymes in a series of steps:
- Three steps – retinol esters convert to retinol. Retinol converts to retinaldehyde. Then, finally, retinaldehyde converts to retinoic acid.
- Two steps – retinol to retinaldehyde. Then, retinaldehyde to retinoic acid.
- One step – retinaldehyde to retinoic acid.
The closer the product is to retinoic acid (e.g., retinaldehyde), the more effective it is and the more readily it converts into retinoic acid for use by the skin.
Forms of retinoids are as follows and go in ascending strength and the conversion pathway, as we’ve seen above:
Retinol Esters
Examples: Retinyl Palmitate, Retinyl Propionate, Retinyl Acetate, Retinyl Linoleate.
Retinyl palmitate is a common OTC. It is the weakest but the safest form of vitamin A. It is suitable for daily use, with very little irritation.
Retinol esters require three steps to convert to retinoic acid. Therefore, it loses most of its potency on the way.
It is generally not used in high enough concentrations to impact skin concerns significantly.
Many products labeled “retinol treatments” use retinyl palmitate instead, so check the ingredients list.
Retinol
Retinol is a common OTC retinoid that treats acne 13 and has anti-aging effects 14-19 by minimizing fine lines and wrinkles and increasing epidermal thickness. Retinol has lots of scientific studies behind it.
The difference between retinol-type ingredients and retinoids is that retinol ingredients are not already in retinoic acid form. They have to be turned into retinoic acid by enzymes on the skin before they can trigger all the cool cell action we discussed earlier. Studies have shown retinol is about 20 times weaker than prescription tretinoin 1.
It works the same as the more potent retinoids but takes longer to get there due to the more conversions required. It is generally found in concentrations of 0.3%, 0.5%, and 1%.
It can be a volatile ingredient that breaks down when exposed to heat, light, and air. That’s why looking for products with encapsulated retinol, airless pump packaging, and opaque containers is a good idea.

Retinoic Acid Esters
Within this category, you have Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate (HPR), an oil-based ester. It is directly related to retinoic acid and can bind directly to the retinoid receptors of the skin cells. It is often found in higher concentrations because of it being an ester.
Hydroxypinacolone retinoate (HPR), found in “Granactive Retinoid” mixes, might be an effective acne treatment and anti-aging ingredient. It is a generally well-tolerated OTC retinoid that should be easy to introduce.
However, most clinical studies combined HPR with other retinoids, making it difficult to tell how significant the effects of HPR are 8-12.
You also may see Retinyl Retinoate, the child of retinol and retinoic acid. It’s a relatively new product to the market that is more stable and active than retinol (8x stronger than retinol, to be precise!). It’s suitable for sensitive skin types as it has a low to medium potential for irritation.
Retinaldehyde
Retinaldehyde, also called retinal, is an OTC retinoid with anti-aging benefits 20, increases epidermal thickness, increases elasticity, has antimicrobial properties, and may treat acne 21.
Retinaldehyde has a medium potential for irritation. It is usually found in concentrations of 0.01%, 0.03%, 0.05%, and 0.1%. It is very unstable, so it is generally found encapsulated.
Retinaldehyde works 11x faster than Retinol and is the strongest retinoid form available without prescription.
Adapalene (Differin)
Previously only available with a prescription, Differin Gel is one of the most lauded formulas for acne treatment. It is a newer, synthetic retinoid that you can buy over-the-counter (OTC) in the U.S. but is prescription-only in many other countries.
Dr. Jenny Sobera, FAAD, Co-Founder and Chief Medical Officer of FaceMD, has been recommending the product to patients for years. “With regular use, you can typically expect to see improvement when clearing acne, as well as improved texture.”
It is less irritating than tretinoin. Its magic lies in its remarkable ability to combat acne. It’s more effective than tretinoin, and the skin better tolerates it. However, it still can cause dryness, flakiness, redness, and stinging in the first few months! It decreases oiliness 26, although it may not be as effective against wrinkles. It doesn’t need to convert into retinoic acid before it becomes active.
Whether adapalene is an efficient anti-aging ingredient like other retinoids comes up quite often. A few studies look promising, although each has limitations, such as a lack of control or an absence of objective measurements. Unfortunately, there doesn’t appear to be enough research to give a decisive answer one way or the other, at least for the time being 27-28.

Tretinoin
Tretinoin, today’s article’s subject, is a well-studied retinoid.
No conversions are required. Also known as all-trans retinoic acid, tretinoin is a metabolite of Vitamin A. It is produced in the body from other retinoids ingested, such as retinol, retinyl esters, and carotenoids. Tretinoin is prescription-only in the U.S. and most countries, with brand names such as Atralin, Avita, Retin-A, Retin-A Micro, and Renova.
Tretinoin works immediately as you apply it to the skin, has a high potential for irritation, and can cause swelling. Tretinoin has 0.025%, 0.05% and 0.1% strengths, but moving up should be done under the care of a dermatologist.
It treats acne 25, hyperpigmentation 29-36, has anti-aging effects 29-39, minimizes fine wrinkles, and increases epidermal, dermal, and granular cell layer thickness. Tretinoin may also reduce pore size 39.
Tazarotene
Third-generation retinoid, Tazarotene, also known under the brand name Avage or Tazorac, is a prescription-only retinoid that treats acne 25, 41, hyperpigmentation 33, 41-42, has anti-aging effects 33, 41-42, and minimizes fine lines and wrinkles.
Tazarotene is stronger than adapalene and may reduce pore size 42.
Tazarotene may be a better wrinkle reducer than tretinoin. It is also potentially more efficacious than tretinoin at treating papules and open comedones and can be used to treat psoriasis. More research is needed.
Isotretinoin
Topical isotretinoin is a retinoid that treats acne 44, has anti-aging effects, minimizes fine lines and wrinkles, and increases epidermal thickness 43. It is prescription-only in most countries.
Accutane is taken orally and is extraordinarily effective against acne, although it has serious side effects.
Tretinoin Safety & Side Effects

It is possibly not safe to use while breastfeeding or while pregnant!
Isotretinoin (Accutane) has teratogenic effects, meaning it causes birth defects. So, with an abundance of caution, medical providers also recommend avoiding tretinoin while pregnant.
Due to the poor absorption of tretinoin from the skin, studies suggest that the risk of malformations in human fetuses after topical tretinoin is smaller. Still, it is recommended to err on the safe side and not use tretinoin while pregnant or breastfeeding.
Side effects include skin discoloration, blistering, facial swelling, burning, conjunctivitis, and eye swelling. These side effects are rare and should be treated immediately by a doctor. Serious side effects of tretinoin are rare.
A small percentage of people who use tretinoin may have an allergic reaction. This can cause rashes, swelling, and difficulty breathing. These side effects are rare and should be treated immediately by a doctor.
Benefits of Tretinoin for the Skin

Tretinoin is a fantastic tool that can deliver healthy-looking, beautiful skin, including a host of benefits when used correctly.
Most subjects develop a healthy-looking “tret glow,” and skin tone irregularities may even out.
Tretinoin has been shown to have scientifically proven effects on the skin:
- Treating and preventing acne vulgaris;
- Minimizes fine lines and wrinkles by increasing collagen synthesis and preventing its breakdown for more youthful, plump, and smooth-looking skin.
- Improves skin texture by increasing cell turnover. This is done at a cellular level instead of acids that work superficially on dead skin cells. The result of retinoids increasing cell turnover is a smoother, brighter skin surface.
- lightening effect – anti-yellowish skin;
- A more even complexion is achieved by decreasing melanin production. This leads to a more even skin tone and reduced appearance of acne scars, sun spots, and hyperpigmentation.
- Clears clogged pores (via cellular exfoliation) by decreasing sebum production.
- Treating shallow indented scarring;
- Increasing epidermal thickness;
- Aids in melasma treatment;
- Aids in vitiligo treatment.
Tretinoin for Acne

Tretinoin helps regenerate skin cells and prevents the clogging of follicles (pores). Tretinoin helps prevent blackheads, whiteheads, and inflamed acne lesions by decreasing follicular plugging.
Acne improvement may take at least 12-16 weeks to see full benefits from tretinoin.
Tretinoin for Anti-aging

Cell turnover doesn’t slow down until you hit your 30s. Before you reach the age of 30, your cells turn over every 28 days. So, if you’re thinking about age-delaying benefits then you could wait until you start heading towards that age zone.
After the age of 30 it is a different matter. Cell turnover can slow down to every 50, 60 or even 70 days. Slower cell turnover leads to skin that is dry, dull and wrinkled! So, your retinoids basically trick your skin into thinking it is younger than it is by increasing the speed of cell turnover.
We have also seen previously, that retinoids provide other benefits aside from age-delaying. So, starting in your 20s if you have acne-prone, oily or sun-damaged skin may be beneficial to you but it might be worth starting with the weaker forms first. Also if you smoke, regularly sunbathe or are generally unhealthy you may want to begin with some form of vitamin A before you reach your 30s.
Tretinoin acts by various mechanisms in skin aging to fight dark spots and wrinkles. Additionally, it has been shown to promote smoother, tighter, and fuller skin by stimulating the production of collagen and glycosaminoglycans.
Visible signs of wrinkles and some coarse wrinkles may improve by 4-6 months of use.
Tretinoin for Hyperpigmentation

Tretinoin helps with hyperpigmentation. It decreases the darkness of brown spots by reducing epidermal pigmentation. Also, it pinkens sallow skin.
Sun-induced brown spots, mottled hyperpigmentation, and freckles may lighten 4-6 months after treatment.
What Is Tretinoin Not Good For?
- Reducing redness – increased vascularity means redness can increase for some;
- Soothing irritation – tretinoin is one of the most irritating ingredients;
- PIE (Post-irritation erythema) is the dilation of the blood vessels. Tretinoin increases vascularity, making erythema worse. If you have pale skin, this looks like redness. If you have darker skin, this can look like a “glow.” If you’re pale, azelaic acid, niacinamide, and vitamin C are better for hyperpigmentation.
How to Use Tretinoin?
When you start tretinoin, it’s best to stop using other active ingredients (other than sunscreen actives, which are especially important now) so you don’t overdo it and irritate your skin.
Tretinoin is powerful and addresses everything from acne to aging, so it’s not a bad idea to strip your routine back at first and then slowly add other actives. After about three months of using tretinoin, I could reintroduce my weekly mandelic acid peel (though I skipped the retinoid the day before and the day of the peel) without irritation.
If your skin is especially sensitive or dry, you may want to start slowly to ease your skin into the extra-strength skin treatment. My derm advised me that tretinoin is still effective if used every other night or even every third night, so if you’re experiencing redness or irritation, step back to alternating nights to give your skin a break. Give your face extra TLC on off nights with a gentle cleanser and a heavy, bland moisturizer.
Studies show that moisturizing before applying tretinoin can improve tolerance and does not interfere with effectiveness. If you want to learn more about different ways of using tretinoin for optimal results, read our guide, Tretinoin Skincare Routine – Designed for Absolutely No Irritation.
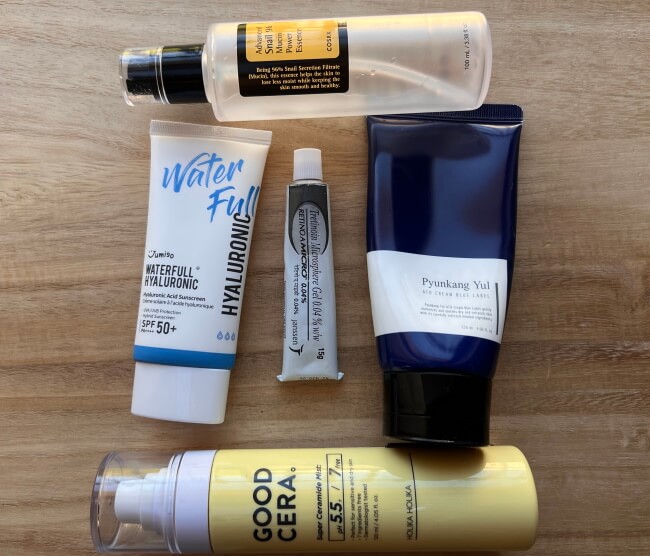
Morning
- Holika Holika Good Cera Super Ceramide Mist
- COSRX – Advanced Snail 96 Mucin Power Essence
- Moisturize
- Use a broad spectrum SPF 50+ sunscreen and avoid sunlight if unprotected.
Read more on why you must use sunscreen while on tretinoin.
Evening
- Cleansing
- Hydrate
- Thoroughly moisturize
- Let face dry
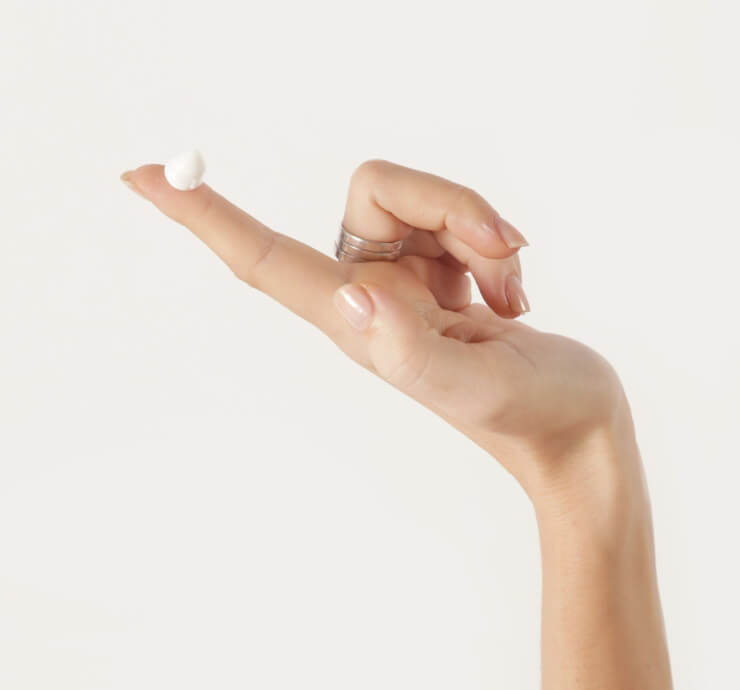
- Apply a pea-sized amount of tretinoin to the face.
- Rub lightly into the whole face, but avoid the eyelids.
- Moisturize
The Tretinoin Purge
For some users, starting tretinoin sometimes leads to a phase known as the tretinoin purge. During this stage, acne, which tretinoin aims to treat, may worsen, resulting in various manifestations, such as occasional whiteheads and more severe breakouts.
If your skin is acne-prone, be prepared for increased acne during the first couple of weeks on tretinoin. This is the “purge” you hear about. The upper layers of your skin are getting sloughed off, bringing underground acne infections to the surface. It should go away soon.
But, if you’ve started tretinoin for anti-aging purposes and don’t usually have acne, you shouldn’t experience purging. Tretinoin brings “brewing” pimples to the surface. If nothing is brewing, there’s nothing to purge.
Guide on Tretinoin Purging to distinguish between breaking out from irritation and tretinoin purging
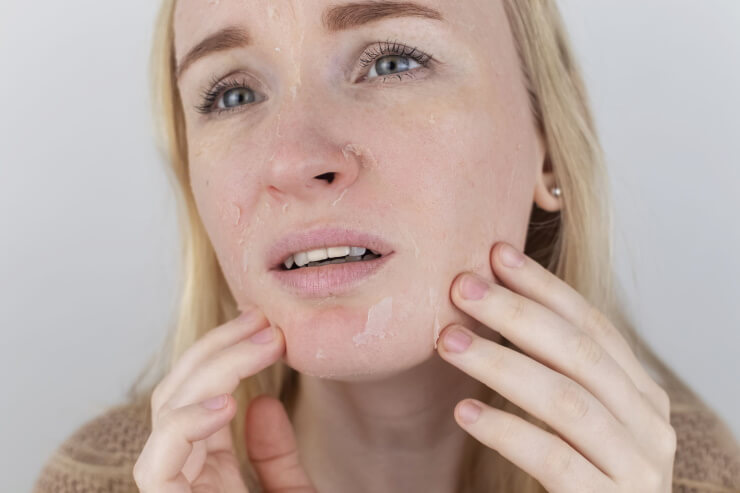
Tretinoin Peeling
One of the biggest culprits of the retinoid “uglies” is dry, flaky skin. As your cell turnover rate increases, expect to see flakes, flakes, flakes for a little bit. It’s normal, and your skin will look fresh and glowy when you’re through with it.
In the meantime, you can eliminate flakes with a mild (I said MILD!) physical exfoliant.

Some good options are a Konjac sponge or a gentle exfoliating powder cleanser. Use sparingly (I did a quick scrub once a week) and gently slough flakes away without irritating your sensitized skin.
Tretinoin Irritation
Depending on the strength of the tretinoin you are using, you may see redness, dryness, patches of flaking skin, and generally irritated and sensitized skin. This is a process called retinisation (the process through which your skin gets used to topical retinoids).
When the dose and the concentration of tretinoin are low, such irritation tends to be mild. But, if irritation develops, it could be a sign that you’ve damaged your skin barrier, and you need to stop treatment and take care of your skin barrier.
The most common side effects are:
- irritation;
- erythema;
- redness;
- sun sensitivity (retinoids should be applied at night).
These are all normal outcomes of beginning retinoids. To counteract this, you can buffer (weaken the formula) the retinoid that you are using by adding in a layer of moisturizer either before or after you have used the product. You can also use oils such as squalane and jojoba over the top of your retinoid product, as these oils won’t interfere with how the retinoid works. You may use Aquaphor or Vaseline if irritation occurs at the corners of the mouth or eyes.
After restarting with tretinoin:
- Use smaller amounts of cream;
- Use it once every 2-3 days;
- Use low-strength tretinoin until your skin is accustomed to the medication’s effects;
- Hydrate more
- Moisturize more
- Protect with SPF
Tolerance usually improves with continued use in 3-4 weeks. Then you can use tretinoin nightly.
Tretinoin and Sunscreen

Sunscreen is a MUST with tretinoin. If you start tretinoin, this is non-negotiable. I probably don’t have to re-iterate, but tanning is also out of the question.
You must commit to using sunscreen every day. Yes, even if it’s winter, even if you have dark skin or don’t enjoy it. Make-up SPF is not enough.
If you can’t commit to wearing sunscreen daily, tretinoin is not for you.
Tretinoin and Actives

When you’re starting tretinoin, to avoid more irritation, stop all other actives: morning and night.
Unless stated otherwise by your medical provider, stop other actives at least one week before starting tretinoin. That means no:
You’re the expert on your skin type and must decide what works for you, but please start slowly and be very gentle.
Once you’ve been using tretinoin for 6+ months, you can add these back in as needed.
Hair Removal on Tretinoin
Above all, don’t wax hair off skin treated with tretinoin. It can tear off part of your skin. It is terrible, gross, and painful, and please don’t wax tretinoin-treated skin. I’ve done it. I’m trying to forget it.
Opt for plucking, shaving, or threading instead.
Skin treated with tretinoin may become sensitive to procedures such as peels, waxing, laser, or microdermabrasion. Stop tretinoin for at least 2-3 days before receiving facial treatments. Please inform your aesthetician of your use of tretinoin before receiving these treatments.
Final Thoughts
Remember, your doctor’s instructions trump everything you read on the internet. He or she is best suited to advise you on your skincare regime.
Tretinoin is considered the gold standard in anti-aging technology. New, promising, exciting stuff is always coming out, but the big challenge for these new ingredients is, can they measure up to retinoids? The answer is usually no. Tretinoin works. And it’s affordable, especially with health insurance.
Show Me Proof
- Cosmetic Dermatology – Baumann
- Schorr, Ethlynn S., Farzi Sidou, and Nabil Kerrouche. “Adjunctive use of a facial moisturizer SPF 30 containing ceramide precursor improves tolerability of topical tretinoin 0.05%: a randomized, investigator-blinded, split-face study.” Journal of Drugs in Dermatology: JDD 11, no. 9 (2012): 1104-1107.
- Moisturizer improves tolerability for tazarotene and does not negatively impact efficacy. Tanghetti, Emil, et al. Poster presented at 32nd Annual Hawaii Dermatology Seminar. 2008.
https://dermatologyandlasersurgery.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/2008-Poster-Moisturizer-Use-Enhances-Facial-Tolerability.pdf - The Role of Skin Care as an Integral Component in the Management of Acne Vulgaris: Part 1: The Importance of Cleanser and Moisturizer Ingredients, Design, and Product Selection. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013 Dec; 6(12): 19–27.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3997205/ - The Role of Skin Care as an Integral Component in the Management of Acne Vulgaris: Part 2: Tolerability and Performance of a Designated Skin Care Regimen Using a Foam Wash and Moisturizer SPF 30 in Patients with Acne Vulgaris Undergoing Active Treatment. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013 Dec; 6(12): 28–36.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3997206/ - Draelos, Zoe Diana (2008) Clinical Situations Conducive to Proactive Skin Health and Anti-Aging Improvement. Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings. Vol. 13. No. 1. Elsevier, 2008.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022202X15526675 - Schorr ES1, Sidou F, Kerrouche N. (2012) Adjunctive use of a facial moisturizer SPF 30 containing ceramide precursor improves tolerability of topical tretinoin 0.05%: a randomized, investigator-blinded, split-face study. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology : JDD, 01 Sep 2012, 11(9):1104-1107
https://europepmc.org/article/med/23135655 - Bettoli V, Zauli S, Borghi A, Toni G, Ricci M, Bertoldi AM, Virgili A. Efficacy and safety of a 12-month treatment with a combination of hydroxypinacolone retinoate and retinol glycospheres as maintenance therapy in acne patients after oral isotretinoin. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2017 Feb;152(1):13-17. doi: 10.23736/S0392-0488.16.05201-9. Epub 2016 Feb 18. PMID: 26889724.
- Veraldi S, Barbareschi M, Guanziroli E, Bettoli V, Minghetti S, Capitanio B, Sinagra JL, Sedona P, Schianchi R. Treatment of mild to moderate acne with a fixed combination of hydroxypinacolone retinoate, retinol glycospheres and papain glycospheres. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2015 Apr;150(2):143-7. PMID: 25876142.
- Truchuelo MT, Jiménez N, Jaén P. Assessment of the efficacy and tolerance of a new combination of retinoids and depigmenting agents in the treatment of melasma. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2014 Dec;13(4):261-8. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12110. PMID: 25399618.
- Ruth, N., & Mammone, T. (2018). Antiaging effects of retinoid hydroxypinacolone retinoate on skin models. Journal Of The American Academy Of Dermatology, 79(3), AB44. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2018.05.215
- Truchuelo, M., Jiménez, N., Miguel-Gomez, L., Hermosa, A., Sánchez-Neila, N., & Cuevas, J. (2017). Histological and Immunohistochemical Evaluation of the Efficacy of a New Cosmetic Formulation in the Treatment of Skin Photoaging. Dermatology Research And Practice, 1-10. doi:10.1155/2017/8407247
- Ruamrak C, Lourith N, Natakankitkul S. Comparison of clinical efficacies of sodium ascorbyl phosphate, retinol and their combination in acne treatment. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2009 Feb;31(1):41-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2494.2008.00479.x. PMID: 19134126.
- Shao Y, He T, Fisher GJ, Voorhees JJ, Quan T. Molecular basis of retinol anti-ageing properties in naturally aged human skin in vivo. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2017 Feb;39(1):56-65. doi: 10.1111/ics.12348. Epub 2016 Jul 4. PMID: 27261203; PMCID: PMC5136519.
- Kang S, Duell EA, Fisher GJ, Datta SC, Wang ZQ, Reddy AP, Tavakkol A, Yi JY, Griffiths CE, Elder JT, et al. Application of retinol to human skin in vivo induces epidermal hyperplasia and cellular retinoid binding proteins characteristic of retinoic acid but without measurable retinoic acid levels or irritation. J Invest Dermatol. 1995 Oct;105(4):549-56. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12323445. PMID: 7561157.
- Kong R, Cui Y, Fisher GJ, Wang X, Chen Y, Schneider LM, Majmudar G. A comparative study of the effects of retinol and retinoic acid on histological, molecular, and clinical properties of human skin. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2016 Mar;15(1):49-57. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12193. Epub 2015 Nov 18. PMID: 26578346.
- Kafi R, Kwak HS, Schumacher WE, Cho S, Hanft VN, Hamilton TA, King AL, Neal JD, Varani J, Fisher GJ, Voorhees JJ, Kang S. Improvement of naturally aged skin with vitamin A (retinol). Arch Dermatol. 2007 May;143(5):606-12. doi: 10.1001/archderm.143.5.606. PMID: 17515510.
- Bellemère G, Stamatas GN, Bruère V, Bertin C, Issachar N, Oddos T. Antiaging action of retinol: from molecular to clinical. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2009;22(4):200-9. doi: 10.1159/000231525. Epub 2009 Jul 31. PMID: 19648781.
- Tucker-Samaras S, Zedayko T, Cole C, Miller D, Wallo W, Leyden JJ. A stabilized 0.1% retinol facial moisturizer improves the appearance of photodamaged skin in an eight-week, double-blind, vehicle-controlled study. J Drugs Dermatol. 2009 Oct;8(10):932-6. PMID: 19852122.
- Diridollou S, Vienne MP, Alibert M, Aquilina C, Briant A, Dahan S, Denis P, Launais B, Turlier V, Dupuy P. Efficacy of topical 0.05% retinaldehyde in skin aging by ultrasound and rheological techniques. Dermatology. 1999;199 Suppl 1:37-41. doi: 10.1159/000051377. PMID: 10473959.
- Pechère M, Germanier L, Siegenthaler G, Pechère JC, Saurat JH. The antibacterial activity of topical retinoids: the case of retinaldehyde. Dermatology. 2002;205(2):153-8. doi: 10.1159/000063903. PMID: 12218231.
- E. Grosshans, R. Marks, J.M. Mascaro, H. Torras, J. Meynadier, M. Alirezai, A.Y. Finlay, P. Soto, M. Poncet, M. Verschoore, A. Clucas, Evaluation of clinical efficacy and safety of adapalene 0·1% gel versus tretinoin 0·025% gel in the treatment of acne vulgaris, with particular reference to the onset of action and impact on quality of life, British Journal of Dermatology, Volume 139, Issue s52, 1 September 1998, Pages 26–33, https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2133.1998.1390s2026.x
- Thiboutot D, Pariser DM, Egan N, Flores J, Herndon JH Jr, Kanof NB, Kempers SE, Maddin S, Poulin YP, Wilson DC, Hwa J, Liu Y, Graeber M; Adapalene Study Group. Adapalene gel 0.3% for the treatment of acne vulgaris: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, controlled, phase III trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006 Feb;54(2):242-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2004.10.879. PMID: 16443054.
- Nyirady J, Grossman RM, Nighland M, Berger RS, Jorizzo JL, Kim YH, Martin AG, Pandya AG, Schulz KK, Strauss JS. A comparative trial of two retinoids commonly used in the treatment of acne vulgaris. J Dermatolog Treat. 2001 Sep;12(3):149-57. doi: 10.1080/09546630152607880. PMID: 12243706.
- Leyden JJ, Shalita A, Thiboutot D, Washenik K, Webster G. Topical retinoids in inflammatory acne: a retrospective, investigator-blinded, vehicle-controlled, photographic assessment. Clin Ther. 2005 Feb;27(2):216-24. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2005.02.009. PMID: 15811485.
- Ellis CN, Millikan LE, Smith EB, Chalker DM, Swinyer LJ, Katz IH, Berger RS, Mills OH Jr, Baker M, Verschoore M, Loesche C. Comparison of adapalene 0.1% solution and tretinoin 0.025% gel in the topical treatment of acne vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 1998 Oct;139 Suppl 52:41-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.1998.1390s2041.x. PMID: 9990420.
- Kang S, Goldfarb MT, Weiss JS, Metz RD, Hamilton TA, Voorhees JJ, Griffiths CE. Assessment of adapalene gel for the treatment of actinic keratoses and lentigines: a randomized trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003 Jul;49(1):83-90. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2003.451. PMID: 12833014.
- Bagatin E, Gonçalves HS, Sato M, Almeida LMC, Miot HA. Comparable efficacy of adapalene 0.3% gel and tretinoin 0.05% cream as treatment for cutaneous photoaging. Eur J Dermatol. 2018 Jun 1;28(3):343-350. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2018.3320. PMID: 30105991.
- Griffiths CE, Finkel LJ, Ditre CM, Hamilton TA, Ellis CN, Voorhees JJ. Topical tretinoin (retinoic acid) improves melasma. A vehicle-controlled, clinical trial. Br J Dermatol. 1993 Oct;129(4):415-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1993.tb03169.x. PMID: 8217756.
- Bulengo-Ransby SM, Griffiths CE, Kimbrough-Green CK, Finkel LJ, Hamilton TA, Ellis CN, Voorhees JJ. Topical tretinoin (retinoic acid) therapy for hyperpigmented lesions caused by inflammation of the skin in black patients. N Engl J Med. 1993 May 20;328(20):1438-43. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199305203282002. PMID: 8479462.
- Griffiths CE, Goldfarb MT, Finkel LJ, Roulia V, Bonawitz M, Hamilton TA, Ellis CN, Voorhees JJ. Topical tretinoin (retinoic acid) treatment of hyperpigmented lesions associated with photoaging in Chinese and Japanese patients: a vehicle-controlled trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994 Jan;30(1):76-84. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(94)70011-7. PMID: 8277035.
- Weinstein GD, Nigra TP, Pochi PE, Savin RC, Allan A, Benik K, Jeffes E, Lufrano L, Thorne EG. Topical tretinoin for treatment of photodamaged skin. A multicenter study. Arch Dermatol. 1991 May;127(5):659-65. PMID: 2024983.
- Kang S, Leyden JJ, Lowe NJ, Ortonne JP, Phillips TJ, Weinstein GD, Bhawan J, Lew-Kaya DA, Matsumoto RM, Sefton J, Walker PS, Gibson JR. Tazarotene cream for the treatment of facial photodamage: a multicenter, investigator-masked, randomized, vehicle-controlled, parallel comparison of 0.01%, 0.025%, 0.05%, and 0.1% tazarotene creams with 0.05% tretinoin emollient cream applied once daily for 24 weeks. Arch Dermatol. 2001 Dec;137(12):1597-604. doi: 10.1001/archderm.137.12.1597. PMID: 11735710.
- Olsen EA, Katz HI, Levine N, Shupack J, Billys MM, Prawer S, Gold J, Stiller M, Lufrano L, Thorne EG. Tretinoin emollient cream: a new therapy for photodamaged skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992 Feb;26(2 Pt 1):215-24. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(92)70030-j. PMID: 1552056.
- Leyden JJ, Grove GL, Grove MJ, Thorne EG, Lufrano L. Treatment of photodamaged facial skin with topical tretinoin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989 Sep;21(3 Pt 2):638-44. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70231-0. PMID: 2674225.
- Griffiths CE, Kang S, Ellis CN, Kim KJ, Finkel LJ, Ortiz-Ferrer LC, White GM, Hamilton TA, Voorhees JJ. Two concentrations of topical tretinoin (retinoic acid) cause similar improvement of photoaging but different degrees of irritation. A double-blind, vehicle-controlled comparison of 0.1% and 0.025% tretinoin creams. Arch Dermatol. 1995 Sep;131(9):1037-44. PMID: 7544967.
- L. LEVER, P. KUMAR, R. MARKS, Topical retinoic acid for treatment of solar damage, British Journal of Dermatology, Volume 122, Issue 1, 1 January 1990, Pages 91–98, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.1990.tb08244.x
- Weiss JS, Ellis CN, Headington JT, Tincoff T, Hamilton TA, Voorhees JJ. Topical tretinoin improves photoaged skin. A double-blind vehicle-controlled study. JAMA. 1988 Jan 22-29;259(4):527-32. Erratum in: JAMA 1988 Aug 19;260(7):926. Erratum in: JAMA 1988 Jun 10;259(22):3274. PMID: 3336176.
- Nyirady J, Bergfeld W, Ellis C, Levine N, Savin R, Shavin J, Voorhees JJ, Weiss J, Grossman R. Tretinoin cream 0.02% for the treatment of photodamaged facial skin: a review of 2 double-blind clinical studies. Cutis. 2001 Aug;68(2):135-42. PMID: 11534915.
- Bershad S, Singer GK, Parente JE, et al. Successful Treatment of Acne Vulgaris Using a New Method: Results of a Randomized Vehicle-Controlled Trial of Short-Contact Therapy With 0.1% Tazarotene Gel. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138(4):481–489. doi:10.1001/archderm.138.4.481
- Machtinger LA, Kaidbey K, Lim J, Loven KH, Rist TE, Wilson DC, Parizadeh DD, Sefton J, Holland JM, Walker PS. Histological effects of tazarotene 0.1% cream vs. vehicle on photodamaged skin: a 6-month, multicentre, double-blind, randomized, vehicle-controlled study in patients with photodamaged facial skin. Br J Dermatol. 2004 Dec;151(6):1245-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.06186.x. PMID: 15606521.
- Kang S, Leyden JJ, Lowe NJ, Ortonne JP, Phillips TJ, Weinstein GD, Bhawan J, Lew-Kaya DA, Matsumoto RM, Sefton J, Walker PS, Gibson JR. Tazarotene cream for the treatment of facial photodamage: a multicenter, investigator-masked, randomized, vehicle-controlled, parallel comparison of 0.01%, 0.025%, 0.05%, and 0.1% tazarotene creams with 0.05% tretinoin emollient cream applied once daily for 24 weeks. Arch Dermatol. 2001 Dec;137(12):1597-604. doi: 10.1001/archderm.137.12.1597. PMID: 11735710.
- Maddin S, Lauharanta J, Agache P, Burrows L, Zultak M, Bulger L. Isotretinoin improves the appearance of photodamaged skin: results of a 36-week, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000 Jan;42(1 Pt 1):56-63. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(00)90009-4. PMID: 10607320.
- Chalker DK, Lesher JL Jr, Smith JG Jr, Klauda HC, Pochi PE, Jacoby WS, Yonkosky DM, Voorhees JJ, Ellis CN, Matsuda-John S, et al. Efficacy of topical isotretinoin 0.05% gel in acne vulgaris: results of a multicenter, double-blind investigation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987 Aug;17(2 Pt 1):251-4. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(87)70200-x. PMID: 2957398.
- Loss MJ, Leung S, Chien A, Kerrouche N, Fischer AH, Kang S. Adapalene 0.3% Gel Shows Efficacy for the Treatment of Atrophic Acne Scars. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2018 Jun;8(2):245-257. doi: 10.1007/s13555-018-0231-8. Epub 2018 Mar 16. PMID: 29549598; PMCID: PMC6002315.